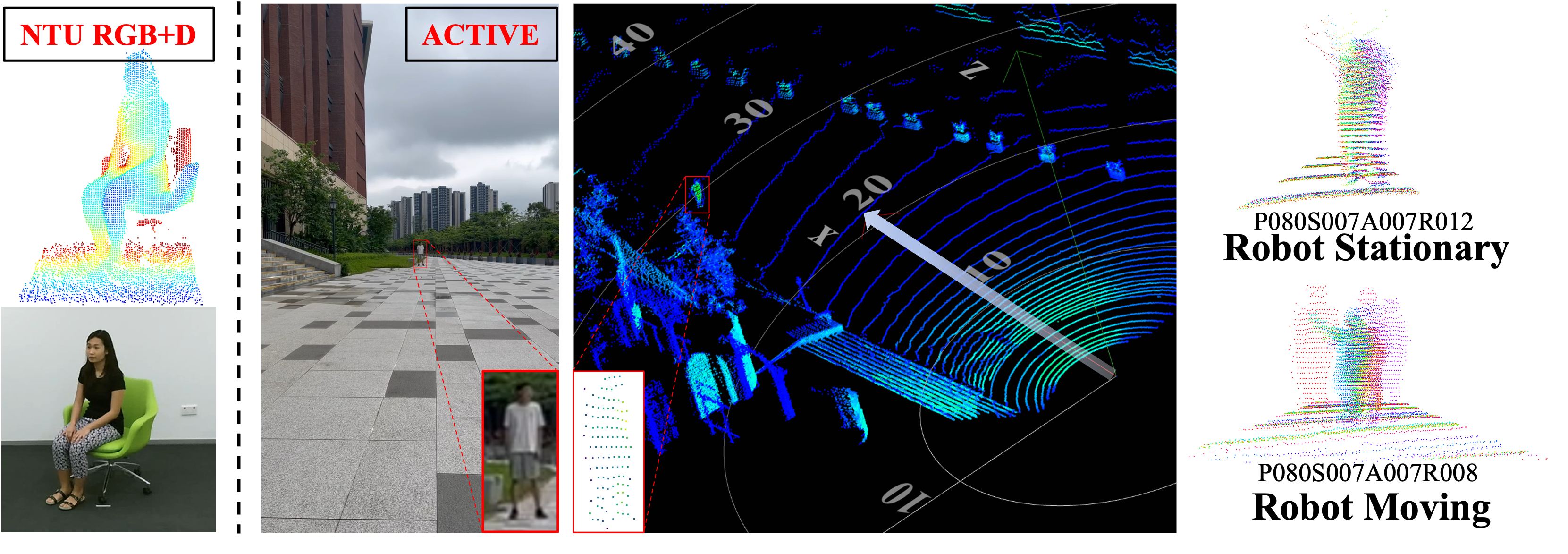
ACTIVE is a large-scale human behavior understanding dataset designed for natural human-robot interaction (N-HRI) scenarios, featuring 46,868 video instances with synchronized RGB and LiDAR point cloud data. It supports both action recognition and human attribute recognition tasks, providing a comprehensive benchmark for long-range, dynamic perception.

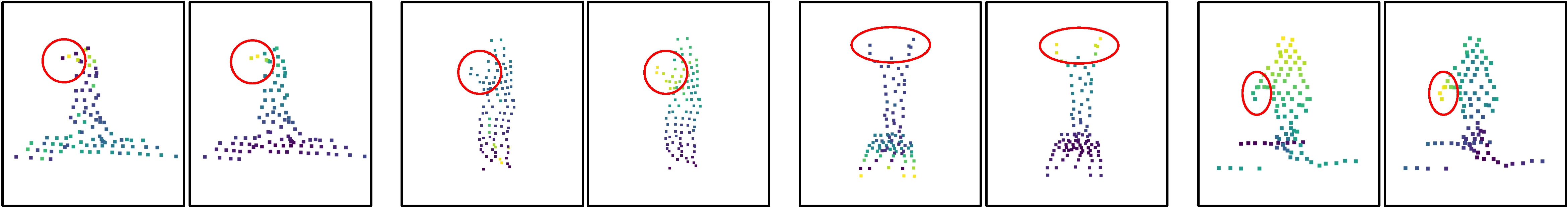
In contrast to NTU RGB+D (left), challenges visible for ACTIVE include: (1) Distance Variation (3-50m), (2) Minor Actions (e.g., looking left), (3) Composite Actions (with simultaneous human motion), and (4) Robot Motion. The images on the right show point cloud accumulation for stationary vs. moving robots (multi-frame overlay), illustrating the challenge of Robot Motion.
| 1. Walking | 2. Raising Arms | 3. Waving | 4. Grasping | 5. Touching |
| 6. Turning Clockwise | 7. Turning Counterclockwise | 8. Calling Over | 9. Shooing Away | 10. Leftward |
| 11. Rightward | 12. Pointing Up | 13. Pointing Down | 14. Clapping | 15. Rubbing Hands |
| 16. Thumbs Up | 17. Nodding | 18. Thumbs Down | 19. Shaking Head | 20. Looking Left |
| 21. Looking Right | 22. Scratching Head | 23. Touching Chin | 24. Arms Crossed | 25. Hands on Waist |
| 26. Stretching | 27. Shrugging Shoulders | 28. Drinking | 29. Phone Call | 30. Texting |
Arms Crossed
Calling Over
Turning Clockwise
Drinking
Leftward
Nodding
Phone Call
Grasping
Pointing Down
Pointing Up
Raising Arms
Hands on Waist
Shrugging Shoulders
Stretching
Texting
Rightward
Thumbs Down
Thumbs Up
Touching Chin
Scratching Head
Touching
Turning Counterclockwise
Waving
Shooing Away
Looking Right
Thumbs Down
Touching Chin
Touching
Turning Clockwise
Waving
Clapping
Grasping
Phone Call
Natural Human-Robot Interaction (N-HRI) requires robots to recognize human actions at various distances and states, while the robot itself may be in motion or stationary. This setup is more flexible and practical than traditional human action recognition tasks. However, existing benchmarks are designed for conventional human action recognition and fail to address the complexities of understanding human action in N-HRI, given the limited data, data modalities, task categories, and diversity in subjects and environments. To understand human behavior in N-HRI, we introduce ACTIVE (Action in Robotic View), a large-scale human action dataset for N-HRI. ACTIVE includes 30 composite action categories with labels, 80 participants, and 46,868 video instances, covering both point cloud and RGB modalities. During data capture, participants perform various human actions in diverse environments at different distances (from 3 m to 50 m), with the camera platform also in motion to simulate varying robot states. This comprehensive and challenging benchmark aims to advance research on human action understanding in N-HRI, such as action recognition and attribute recognition. For recognizing actions in robotic view, we propose ACTIVE-PC, which achieves accurate perception of human actions at long distances through Multilevel Neighborhood Sampling, Layered Recognizers and Elastic Ellipse Query, along with precise decoupling of kinematic interference and human actions. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of this method on the ACTIVE dataset.